We often hear of UPS transformers in reference to static UPS system technology (trafo or trafoless), isolation transformers and transformers for different neutral systems. Frequently however, the purpose of the transformer is not clear and becomes confused, increasing the risk of incorrect technical choices. Here below you will find a short (but not exhaustive) illustration of the main differences and reasons for choosing one solution over another.
UPS technologies with transformer
A common opinion is that the Static UPS system with transformer guarantees galvanic isolation. This is only partly true. In fact, as you can see in Figure 1, isolation is assured exclusively for the inverter line.
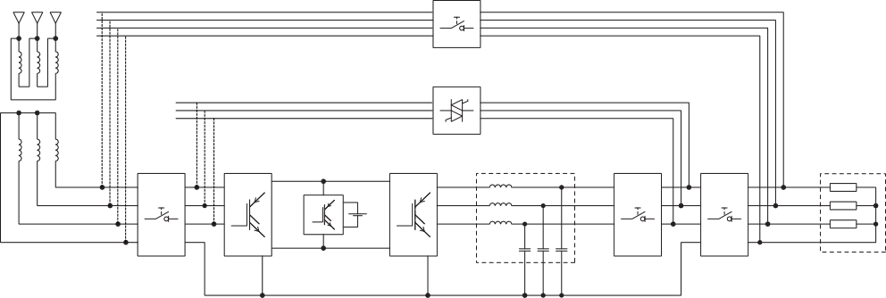
If the bypass line is not isolated, there is no guarantee of any input/output isolation on it. If galvanic separation is required, an additional transformer must be installed on the auxiliary input.
In fact, the transformer is used in the UPS to reconstruct the shape of the sine wave by adapting it to the output voltage value. These UPS can be used with their factory settings in the event of differences in the rectifier supply and the auxiliary supply as well as their neutrals.
When the trafoless UPS requires a transformer
Generally speaking, a UPS does not need a transformer. A UPS without a transformer normally requires a neutral to work. This engineering choice is linked to various factors, including improved yield, minimum floor space and reduced costs.
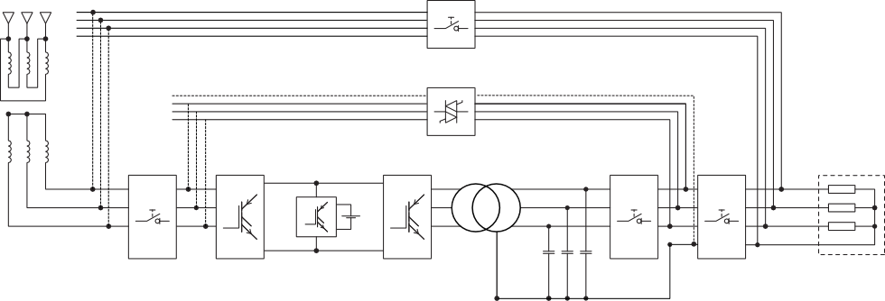
There are however some cases in which a transformer is required for static trafoless UPS:
- when the neutral is not available to create it;
- when there are two separate supplies, in order to avoid the grouping of different neutrals (see Figure 2);
- when galvanic isolation is required and/or the neutral systems need altering
Conclusion
There is no general rule for choosing a UPS with or without a transformer, as the choice is linked to technical and economic considerations concerning the electrical system, as well as purchase and running costs.
The best thing to do is to contact the UPS supplier directly and provide the system features (e.g. presence or not of the neutral, need for isolation or presence of separate distribution networks for the main and auxiliary inputs). The supplier will be able to study the system constraints and propose the best solution.
Tech Info – May 2010
THE UPS AND THE TRANSFORMER
by
MATTEO GRANZIERO
Technical Communication Specialist
SOCOMEC UPS

